Request an Appointment
(703) 719-2040
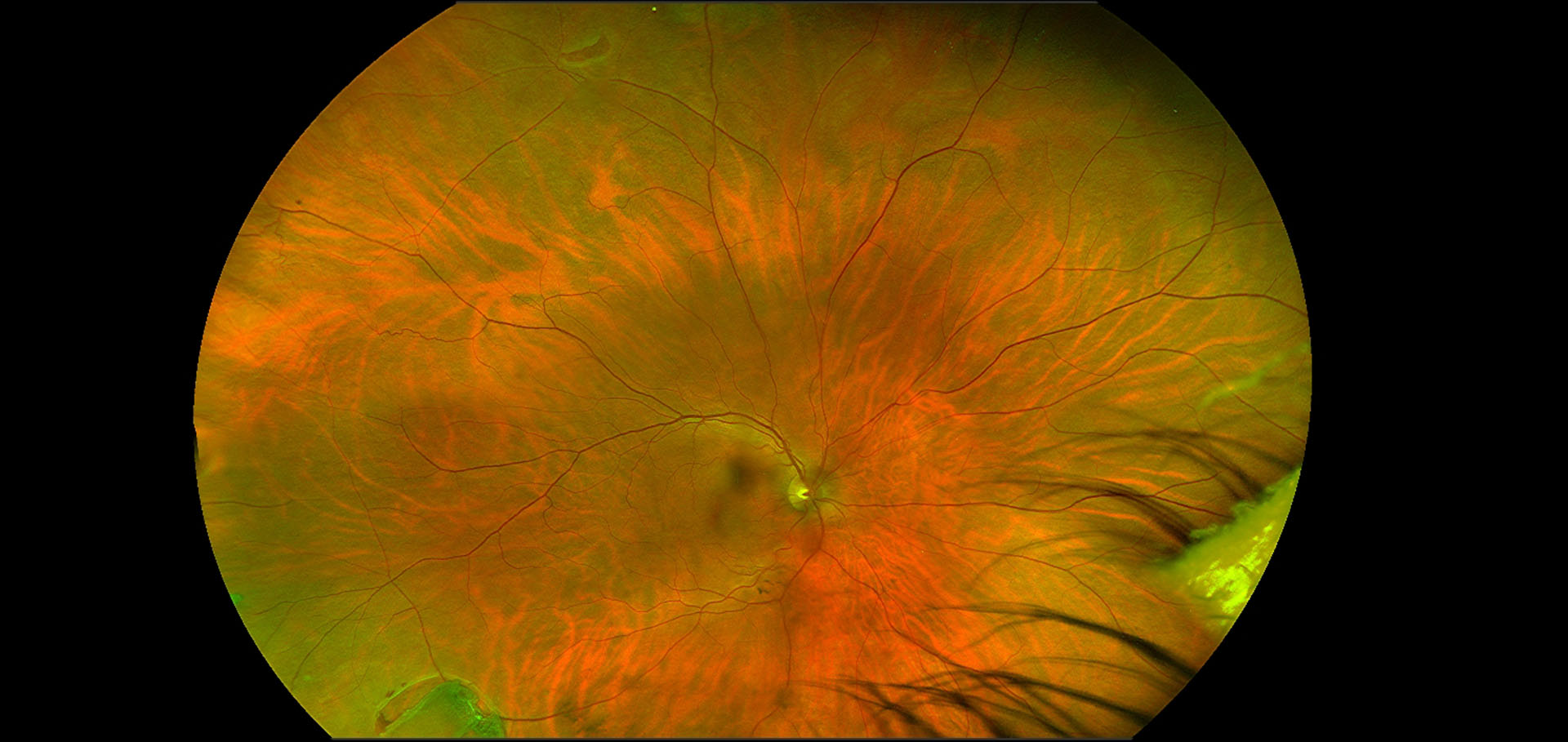
A retinal tear typically occurs with the aging process when the shrinking vitreous fluid in the eyeball causes the retina to tear instead of detaching from the underlying tissue in the back of the eye. While a torn retina can cause a range of vision changes, it can also lead to a retinal detachment with partial or complete vision loss.
With a retinal tear, symptoms can include the sudden onset of floaters and flashes of light. An associated vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment can cause more severe symptoms such as blurred vision and the appearance of a curtain descending over a portion of the visual field. However, in some cases, a retinal tear may not manifest any noticeable symptoms.
If a retinal tear is diagnosed promptly before it progresses to retinal detachment, the prognosis usually is very good. Retinal tears are typically treated with laser. Treatment is performed in an office setting and is very effective and quite safe. These procedures create a demarcation around the tear or break that reduces the risk of the tear progressing to retinal detachment. After a tear has been treated, there remains a future risk of developing additional, separate retinal tears; therefore, continued monitoring is important.
The decision to treat a retinal tear is based on several factors and some tears may be observed without treatment based on consideration of these factors.
